| Normal Lab Values | ||||||
|
|
Microbiology Cases
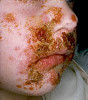
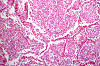
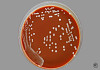
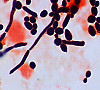
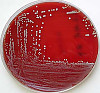
Microbiology/Pathology Case Descriptions Clinical history: Over the course of 1 week, a 6-year-old boy develops 0.5- to 1.0-cm pustules on his face. During the next 2 days, some of the pustules break, forming shallow erosions covered by a honey-colored crust. New lesions then form around the crust. The boy's 40-yearold uncle develops similar lesions after visiting for 1 week during the child's illness. Image Gallery: m1-1. What is the MOST LIKELY diagnosis?
m1-2. The Gram stain from a skin pustule showed gram positive cocci in clusters. The organism grew on sheep blood agar (SBA) and was catalase positive. What is the most likely microorganism? A. Staphylococcus aureus
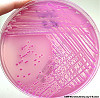
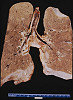
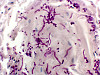
Micro Case 2 (Path Slide 18) Clinical History: This 29-year-old male's illness began 10 weeks prior to death, with an episode of "flu". Two weeks later his urine became "smoky". He was found to have hematuria, albuminuria and elevated BUN (180 mg/dl). He died from a pulmonary embolus. Image Gallery:
m2-1. What is the BEST diagnosis at the time of death?
m2-2. The throat culture obtained exhibited gram positive cocci in chains. It also showed beta-hemolysis on sheep blood agar (SBA) and was catalase negative. What was the most likely organism?
m2-3. An elderly wheelchair bound man had a history of recurrent urinary tract infections. He presents with new onset of fever, chills, and confusion. Blood cultures were drawn. The organism grown was non-hemolytic, catalase negative, and PYR positive. Gram stain showed gram positive cocci. What is the most likely organism?
m2-4. An elderly wheelchair bound man had a history of recurrent urinary tract infections. He presents with new onset of fever, chills, and confusion. Blood cultures were drawn. The organism grown was non-hemolytic, catalase negative, and PYR positive. Gram stain showed gram positive cocci. What is the MOST LIKELY organism?
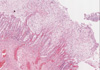
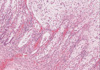
Micro Case 3 (Path Slide 51) Clinical History: A 45-year-old male became ill approximately 2 to 3 weeks ago following an alcoholic spree. He had nausea, vomiting, dehydration, confusion and high fever. He died suddenly shortly after admission. Image Gallery:
What is the MOST LIKELY diagnosis AND the likely causative agent?
m3-1. These images depict pneumonia in the stage of:
m3-2. Community acquired atypical pneumonia can be caused by which of the following organisms?
Micro Case 4 (Path Slide 195) Clinical History: A 67-year-old male had rheumatic heart disease for thirty years. Three months prior to death he began to have episodes of fever and chills accompanied by signs of worsening congestive heart failure. Splinter hemorrhages and purpuric skin rashes were noted three weeks before death. Image Gallery:
m4-1. What is the MOST LIKELY diagnosis?
m4-2. Most cases that present with these findings are caused by:
m4-3. In this particular patient the MOST LIKELY causative organism was:
m4-4. The organism MOST LIKELY to infect normal heart valves is:
m4-5. The organism MOST OFTEN associated with infective endocarditis in IV drug abusers is:
m4-6. The heart valve MOST OFTEN affected by infective endocarditis in IV drug abusers is the:
m4-7. Which of these organisms are normal flora of the throat and are associated with dental caries, brain abscesses, and endocarditis?
m4-8. A patient with suspected infectious endocarditis has a St. Jude’s prosthetic aortic valve and a fever of 38.6°C (101.5°F). Blood culture shows non-hemolytic, small, white colonies. The organism was Gram positive, catalase positive and coagulase negative. What is the MOST LIKELY organism?
m4-9. A throat culture grows normal oropharyngeal flora. What alpha-hemolytic organism is most likely to be isolated on the blood agar? A. Staphylococcus epidermidis
m4-10. A throat culture grows normal oropharyngeal flora. The coagulase test for the organism is positive. What is the genus and species of the organism? A. Staphylococcus aureus
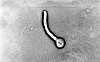
Clinical history: A 33-year-old female dairy farmer develops a severe headache and neck stiffness. On physical examination, her temperature is 38.2°C. She has no papilledema. A lumbar puncture is performed, and a Gram stain of the CSF obtained shows many short, gram-positive rods. Image Gallery: m5-1. Based on the clinical findings presented, what is the most likely causative agent in the case above?
m5-2. A sputum gram stain of an elderly person with cough and fever shows gram positive cocci in pairs. What is the most likely organism?
m5-3. A 10-month-old child of a family from Mexico living in Durham was noted by his mother to have a grand mal seizure with shaking of arms and legs by the description given to the EMT. The EMTs found the child limp and unresponsive. In the emergency room the child’s fever was 39.5°C (103.1°F). Blood cultures and lumbar puncture were performed. CSF findings were as follows:
Gram stain showed PMNs and occasional Gram-negative coccobacillary organisms. The organism grew on chocolate agar but not on sheep blood agar or MacConkey’s agar. What is the most likely organism in this case?
Micro Case 6 (Path Slide 123) Clinical History: A 25 year-old woman had pelvic pain, fever, and vaginal discharge for 3 weeks. On physical examination, she has lower abdominal adnexal tenderness and a painful, swollen left knee. Laboratory studies show WBC count of 11,875/mm3 with 68% segmented neutrophils, 8% bands, 18% lymphocytes, and 6% monocytes. Image Gallery:
m6-1. What is the MOST LIKELY diagnosis AND the likely causative agent? m6-2. What is a likely complication of this disease?
m6-3. What organisms are most likely to cause this disease?
m6-4. Which of the following statement about this disease is FALSE?
m6-5. The following organisms are commonly responsible for pelvic inflammatory disease EXCEPT:
m6-6. A 25-year-old male presents with urethritis. The Gram stain shows intracellular gram positive cocci. What is the most likely organism?
Micro Case 7 (Path Slide 9) Clinical History: A 51-year-old male had a "neurogenic bladder", caused by a spinal cord tumor. He had multiple bladder infections which were treated with antibiotics. He had surgery to remove the tumor. Postoperatively, he developed fever and costovertebral angle tenderness which did not respond to antibiotics. He expired and an autopsy was performed. Image Gallery: m7-1. What is the BEST diagnosis?
m7-2. ALL of the following are risk factors for this condition EXCEPT:
m7-3. A urine culture from an 18-year-old woman with similar symptoms also grew a pure culture of more than 100,000 colonies/ml of an organism on sheep blood agar (SBA) and MacConkey’s agar. The gram stain also showed gram negative rods. What is the most likely organism?
Micro Case 8 (Pathology Slide 39) Clinical History: 58-year-old African American female had been hemiplegic on the right side for 3 months prior to death. She developed malaise, fever and chills after visiting with her grandchildren. Her infection progressed. She developed dyspnea and expired. Image Gallery
m8-1. Based on these clinical findings, what is the best diagnosis and likely causative agent?
m8-2. What is the most likely cause of this disease in most adults?
M8-2. What organism would be most likely to cause a persistent infection in cystic fibrosis?
Clinical history: A 52-year-old homeless, alcoholic man had a fever and a cough productive of thick sputum that worsened over several days. His temperature is 38.2°C. Diffuse crackles are heard at the right lung base. Laboratory studies are as follows:
Image Gallery
m9-1. Based on these clinical findings, what is the likely causative agent? m9-2. An 18-year-old Duke freshman presented to student health with severe headache, fever, and disorientation. A lumbar tap was performed with the following results:
The gram stain of the spinal fluid revealed numerous PMNs with intracellular gram-negative diplococci. What is the most likely organism?
Clinical history: A 66-year-old man incurs extensive thermal burns to his skin and undergoes skin grafting procedures in the surgical intensive care unit. Two weeks later, he has increasing respiratory distress. Laboratory studies show hemoglobin of 13.1 g/dL, hematocrit 39.2%, platelet count 222,200/mm3, and WBC count 4520/mm3 with 15% monocytes. A chest radiograph shows extensive bilateral infiltrates with patchy areas of consolidation.
m10-1. Based on these clinical findings, what is the likely causative agent? m10-2. A sputum specimen from a cystic fibrosis patient grew Gram negative rods on sheep blood agar and MacConkey’s agar. The organism was oxidase positive. What is the most likely organism?
Clinical history: A suspicious envelope arrived for sorting at rural post office. The envelope was opened and found to contain white powder. Approximately two days later, the postal worker who handled the letter developed cutaneous boils, which were and 1 to 5 cm in diameter with central necrosis and eschars. He and his wife also developed a mild nonproductive cough with fatigue, myalgia for 72 hours, followed by severe dyspnea, diaphoresis and cyanosis. Temperature of 39.5°C, pulse 105/min, respiration 25/min, and blood pressure 85/45mm Hg. Crackles were heard at the lung bases. A chest xray shows a widened mediastinum and small pleural effusions. WBC count of 13,130/mm3, hemoglobin 13.7g/dL, hematocrit 41.2%, MCV 91 um3, and platelet count 244,000/mm3. Both died despite antibiotic therapy. Several cattle, horses, and sheep on the postal worker's farm also died. Image Gallery m11-2. In a somewhat related case, when Pharaoh did not heed Moses to the let the captive Hebrews go, a series of plagues fell upon the land of Egypt. In the fifth plague, large domesticated mammals including cattle, horses, and sheep died. This was followed by a plague in which the Egyptians developed cutaneous boils. Some developed a mild nonproductive cough associated with fatigue, myalgia, and low grade fever over 72 hours, followed by a rapid onset of severe dyspnea with diaphoresis and cyanosis. Despite antibiotic therapy with both ciprofloxacin and doxycycline (had they been available), many of those affected would die. Which of the following organisms is most likely to have produced these findings?
Micro Case 12 (UMich Slide 017) Clinical history: A 45-year-old woman is being treated in the hospital for pneumonia complicated by septicemia. She has required multiple antibiotics and was intubated and mechanically ventilated earlier in the course. On day 20 of hospitalization, she has abdominal distention. Bowel sounds are absent, and abdominal radiograph shows dilated loops of small bowel suggestive of ileus. She has a low volume of bloody stool. Image Gallery
m12-1. Based on these clinical findings, what is the likely causative agent? m12-2. Which of the following are appropriate specimen samples for anaerobe culturing:
Clinical history: A 25-year-old man is involved in an accident in which he is ejected from the vehicle. He sustains a compound fracture of the left humerus and undergoes open reduction with internal fixation of the humeral fracture. Several days later, he has marked swelling of the left arm and crepitus. Image Gallery m13-1. In a similar case, a middle aged woman with type 2 diabetes presents to the emergency room with a very painful right lower leg. She has a wound on that extremity and stated that she stumbled on a fallen tree limb in her yard. You observe that her lower leg is discolored and swollen with several areas of crepitus. The abscess fluid was sent to the microbiology laboratory for aerobic and anaerobic culture. The organism grew best on anaerobic cultures and was lecithinase positive. Gram stain shows gram positive rods and the organism show anaerobic growth on egg yolk agar. What is the most likely organism?
Micro Case 14 (Path Slide 451) Clinical History: A 4-year-old female had a gradual onset of fever, productive cough, anorexia and diarrhea about eleven days prior to death. The breath sounds were harsh, and a few cracking rales were heard over the right base posteriorly. Image Gallery:
m14-1. Based on these clinical findings, what is the likely causative agent?
m14-1. Which of the following is the BEST diagnosis?
Clinical history: A 35-year-old man with HIV complains that he has had a "bad" taste in his mouth and discoloration of his tongue for the past 6 weeks. Image Gallery:
m15-1. What is the MOST LIKELY diagnosis? m15-2. In a separate case, a blood culture from a neutropenic (<100 neutrophils/ul) 50-year-old woman on broad spectrum antibiotics grew a yeast. Tests for germ tubes were positive in the microbiology laboratory. What is the likely organism?
Clinical history: A 44-year-old diabetic woman developed facial pain over the past 24 hours. She has become lethargic and obtunded. There is swelling with marked tenderness over the left and right maxilla, bilateral exophthalmos, diffuse abdominal pain, poor skin turgor, and dry mucous membranes. Her temperature is 37.7°C. She has tachycardia, but no murmurs, and tachypnea; the lung fields are clear. Image Gallery:
m16-1. What is the MOST LIKELY diagnosis and the best treatment option? m16-2. In a separate case, A 22-year-old with non-Hodgkins lymphoma was profoundly neutropenic after induction chemotherapy and developed fevers. Broad spectrum IV antibiotic therapy was administered, but fevers continued. Chest x-ray showed new bilaterial fluffy pulmonary infiltrates. A bronchoscopy was performed which showed hyaline, septate hyphae with acute-angle branching. What is the MOST LIKELY organism?
Clinical history: A 50-year-old resident of Phoenix, Arizona, has a cough that has persisted for 1 month. On physical examination, his temperature is 38.1°C. A chest radiograph shows 3.5-cm opacity with central cavitation in the right apical region. An open lung biopsy is performed to exclude cancer. Image Gallery:
m17-1. Which of the following organisms is MOST LIKELY to be responsible for these findings?
Clinical history: For the past 3 weeks, a 52-year-old man has had a chronic cough with a low-grade fever. On physical examination, his temperature is 37.4°C. A chest radiograph shows bilateral, scattered, 0.3- to 2-cm nodules in the upper lobes and hilar adenopathy. A fine needle aspirate of one of the nodules shows inflammation with mononuclear cells, including macrophages that, with PAS or silver stains, show intracellular, 2- to 5-um, rounded, yeast-like organisms. Image Gallery:
m18-1. Which of the following infectious diseases is MOST LIKELY to produce these findings?
Clinical history: For the past month, a 68-year-old patient has had painful oral abcesses, fever, and a cough productive of yellow sputum. On physical examination, there is dullness to percussion at the left lung base. A chest radiograph shows areas of consolidation in the left lower lobe. Despite antibiotic therapy, the course of the disease is complicated by abscess formation, and he dies. Image Gallery:
m19-1. Based on these clinical findings, what is the BEST diagnosis AND the likely causative agent?
m19-2. In a separate case, a middle aged man presented to his physician with a persistent cough of two months following an extended overseas trip to visit relatives. He had also noted a 10 pound weight loss and night sweats. A sputum was sent to the microbiology laboratory for routine bacterial culture and AFB culture. Kinyoun stain of his sputum was positive. What is the likely causative agent?
Clinical history: A 50-year-old man post lung transplant was admitted to hospital with fever, chills and cough. Chest x-ray showed multiple small abscesses within a right middle lobe infiltrate. The patient had been treated with prednisone and azathioprine daily for rejection. Gram stain of a bronchoalveolar lavage of the right middle lobe shows gram positive rods. Modified acid fast stain shows partially acid fast bacilli. Image Gallery:
m20-1. What is the most likely organism?
m20-2. Nocardia species are:
Clinical history: An HIV positive male presented in clinic with confusion and disorientation. He had a fever 38.5°C and photophobia. His CD4 count was 80/ul. A lumbar puncture was performed. It showed 32 WBC/ul with 89% lymphocytes, and 6% monocytes, glucose of 22mg/dl, and protein of 89mg/dl. Gram stain showed yeast and India ink showed a thick capsule. Image Gallery:
m21-1. Which of the following is the most likely pathogen?
m21-2. In a separate case, A 35-year-old man who received kidney transplantation was being treated with cyclosporine, azathioprine, and high doses of corticosteroids. While on this regimen, the patient began to experience headaches and became lethargic. A clinical diagnosis of meningoencephalitis was made. He died 7 days later. Autopsy showed a gelatinous meningeal exudate, and on sectioning of the brain, multiple small cyst-like areas were seen. Microscopic examination showed areas containing rounded structures with a prominent capsule that stained brightly with mucicarmine. Image Gallery: What is the most likely organism?
|
|||
Click here to submit questions or comments about this site. Updated 02/13/13 - Velkey |
|||