CASE NUMBER 521, part 2
Clinical History (continued):
Laboratory analysis shows:
AST: 226 ALT: 287 Alk Phos: 170 T. Bili: 4 Albumin: 2.5
WBC: 7 Hb: 14 HCT: 42 Platelets: 100,000
Hepatitis A Ab: Negative
HBsAg: positive
HBeAg: positive
IgM anti-HBc: positive
Anti-HBs: negative
Hepatitis C PCR: Negative
HIV: Negative
After laboratory assessment, a percutaneous needle biopsy of the liver is performed. A virtual slide and microscopic images from the biopsied material are provided below.
Virtual Slide and Image Gallery:
Slide (UMich_30760nl): [DigitalScope]
Review Liver Histology
Slide 3: Liver
[ImageScope] [DigitalScope]
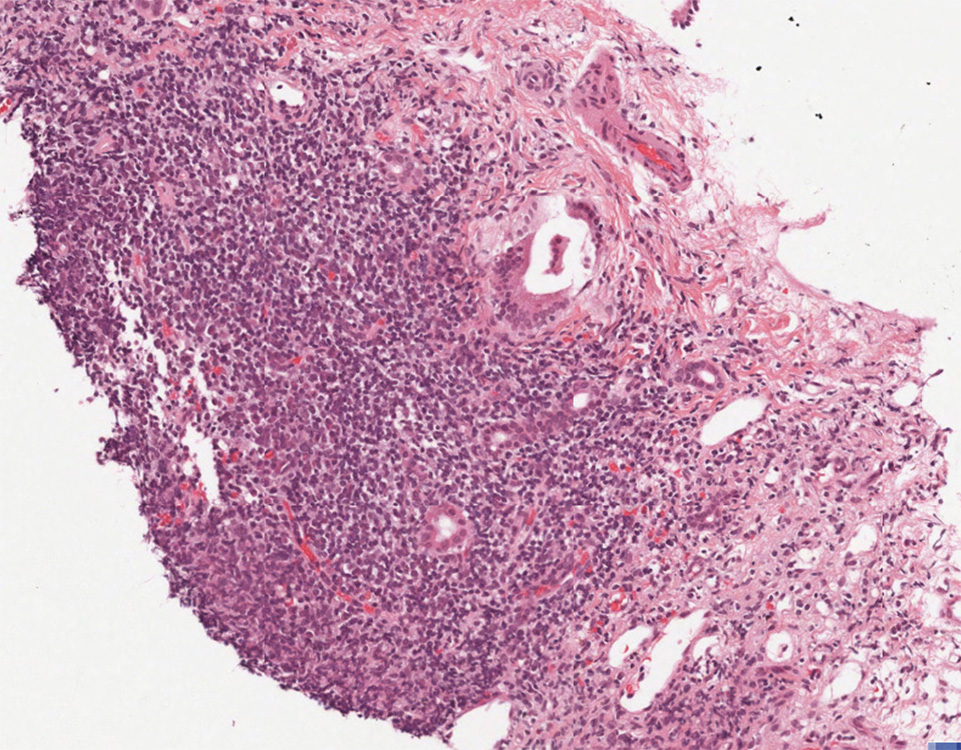
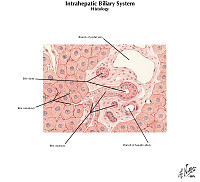
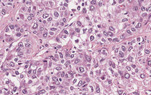
The liver is the organ that metabolizes nutrients received from the digestive tract. These nutrients and processed by tissue hepatocytes which are large polygonal cells. The hepatocyes are separated by portal triads. The triads consist of an artery, a vein and a bile duct. The bile duct is lined by cuboidal epithelium. The artery has a muscular wall and a flat endothelial lining. The sinuses are well defined and contain a small amount of blood.
|
|
Summary of Microscopic Findings
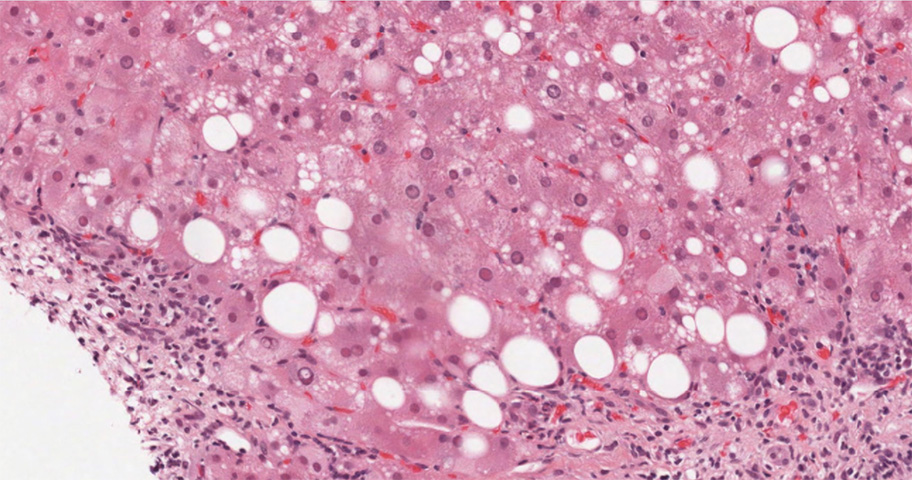
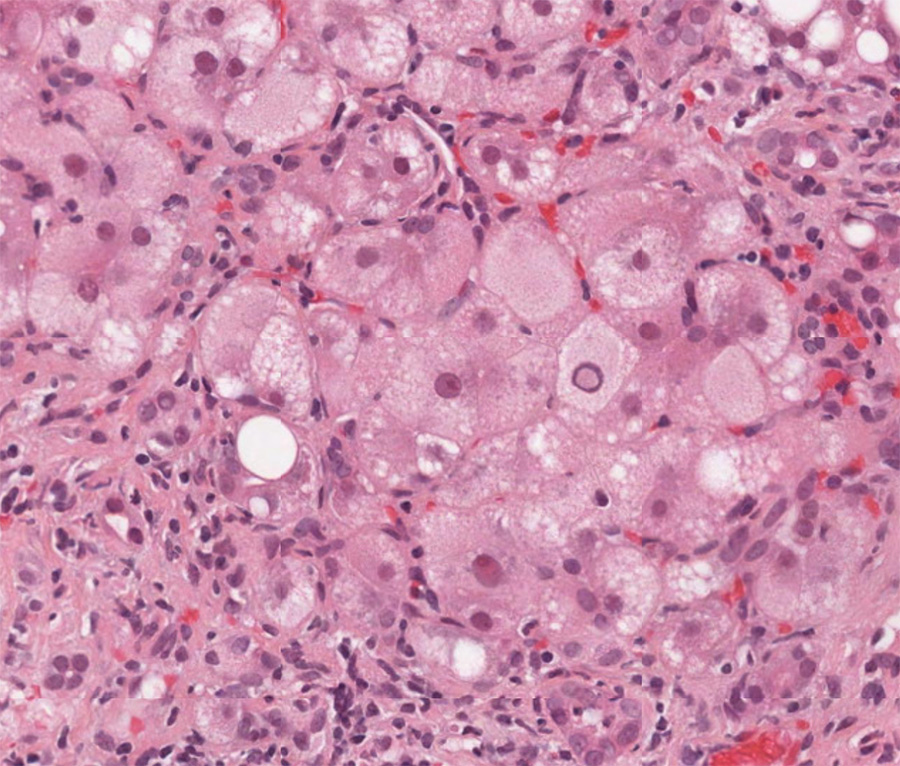
The biopsy demonstrates mild portal and interface hepatitis. The inflammatory infiltrate is compose predominantly of small lymphocytes and scattered plasma cells. No significant interlobular bile duct injury of vascular abnormality is seen. The lobular parenchyma contains small lymphoid aggregates, a rare acidophil body and scattered hepatocellular intracytoplasmic ground glass inclusions. There is only minimal macrovesicular steatosis (less than 5%) and no pigment accumulation.
|
VM image questions:
- Describe the microscopy. Is the inflammation confined to the portal area?
- Take a screenshot and annotate: portal inflammation and steatosis.
- Which type of inflammation is present?
521-3. How do the laboratory values contribute to the differential diagnosis?
--ANSWER--
CASE NUMBER 521, part 3
Clinical History Continued: The patient is then lost to follow up. He returns to the emergency department 15 years later with a 2-day history of hematemesis. Physical exam reveals jaundice and a prominent abdomen with fluid wave. While he is waiting to be admitted to the hospital, he begins vomiting blood and dies. An autopsy is performed and tissue samples are collected for analysis.
Virtual Slide and Image Gallery:
Slide (UMich_30502): [DigitalScope]
Review Liver Histology
Slide 3: Liver
[DigitalScope]
The liver is the organ that metabolizes nutrients received from the digestive tract. These nutrients and processed by tissue hepatocytes which are large polygonal cells. The hepatocyes are separated by portal triads. The triads consist of an artery, a vein and a bile duct. The bile duct is lined by cuboidal epithelium. The artery has a muscular wall and a flat endothelial lining. The sinuses are well defined and contain a small amount of blood.
|
|
Summary of Gross and Clinical Findings
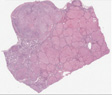
The gross image of the liver shows macronodular cirrhosis with multiple nodules greater than 3 mm.
|
Summary of Microscopic Findings
The section shows cirrhosis mild portal and lobular hepatitis. The inflammatory infiltrate is composed predominantly of lymphocytes. There is no significant interlobular bile duct injury. There are acidophil / apoptotic bodies. There is no significant steatosis (less than 5%). There is a hepatocellular carcinoma in the upper left region. Hepatocellular carcinoma is characterized by abnormal hepatic architecture with by an absence of portal tracts, solid sheets of hepatocytes and unpaired arterioles. Note the cytology of the malignant hepatocytes is not significantly different from that of the hepatocytes outside of the tumor.
|
Gross image questions:
- Describe the gross appearance of the liver. Is the liver normal in size?
- What is the pathophysiology that accounts for the gross findings?
VM image questions: (slide 30502)
- Describe the histologic findings.
- Take a screenshot and annotate: a portal triad and central vein.
- Which process is seen in the majority of the liver?
- How does the subcapsular nodule differ from the rest of the liver? What is the likely process occurring in this nodule?
521-4. What is the final diagnosis?
--ANSWER--
521-5. Which of the following most commonly results in chronic hepatitis?
- Hepatitis A virus
- Hepatitis B virus
- Hepatitis C virus
- Hepatitis D virus
- Hepatitis E virus
- Hepatitis G virus
--ANSWER--
|