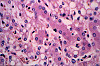
CASE NUMBER 85
[ImageScope] [WebScope]
Clinical History: A 64-year-old morbidly obese white woman was admitted to the emergency department with a 6-hour history of nausea, vomiting and jaw pain. While she was in the emergency department she collapsed and died. Autopsy revealed a massive heart attack as well as significant liver pathology.
Image Gallery:
(Review Normal Histology - click here)
Norm No. 3 Liver
[ImageScope] [WebScope]
The liver is the organ that metabolizes nutrients received from the digestive tract. These nutrients and processed by tissue hepatocytes which are large polygonal cells. The hepatocyes are separated by portal triads. The triads consist of an artery, a vein and a bile duct. The bile duct is lined by cuboidal epithelium. The artery has a muscular wall and a flat endothelial lining. The sinuses are well defined and contain a small amount of blood.
|
|
|
85-1. What is the differential diagnosis?
85-2. Which of the following is commonly associated with this condition?
- Cirrhosis
- Focal nodular hyperplasia
- Hepatitis B infection
- Kayser-Fleischer rings
- Type 2 diabetes
85-3. Which of the following is one of the proposed mechanisms by which insulin resistance contributes to the accumulation of triglycerides in hepatocytes?
- Decreased serum IL-6 and tumor necrosis factor (TNF)
- Decreased synthesis and uptake of fatty acids
- Impaired oxidation of fatty acids
- Increased synthesis of very-low-density lipoprotein cholesterol
- Peroxidation of membrane phospholipids
PANCREAS Review Items
Key Vocabulary Terms (click here to search any additional terms on Stedman's Online Medical Dictionary)
LEARNING OBJECTIVES
Absolutely critical information you must know to practice medicine is in bold font.
Important information that will be needed for routine patient care is in regular font.
Information about less common diseases that you may encounter in clinical practice and that will probably appear on examinations is in italics
- Compare and contrast the clinical and pathologic features of:
- Discuss the clinical and pathologic features of cystic fibrosis.
- Compare and contrast acute and chronic pancreatitis, in terms of:
- etiologic/predisposing factors
- pathogenesis
- morphologic features
- laboratory manifestations
- clinical findings and course
- complications
- Compare and contrast the clinical and pathologic features of adenocarcinoma of the:
- pancreatic head
- pancreatic body/tail
- ampulla of Vater
- 5. Discuss islet cell tumors of the pancreas, in terms of:
- incidence
- morphology
- benignity vs. malignancy
- immunohistochemical characteristics
- endocrine function
- clinical features and course
- Discuss indications and complications of pancreatic islet cell transplantion.
LIVER and BILIARY TRACT Review Items
Key Vocabulary Terms (click here to search any additional terms on Stedman's Online Medical Dictionary)
LEARNING OBJECTIVES
Absolutely critical information you must know to practice medicine is in bold font.
Important information that will be needed for routine patient care is in regular font.
Information about less common diseases that you may encounter in clinical practice and that will probably appear on examinations is in italics
- Describe the formation of bile and explain abnormalities that could cause jaundice.
- Discuss the clinical indications for the following laboratory tests:
- Compare and contrast the clinical and pathologic features of
- Compare and contrast biliary atresia and neonatal hepatitis, in terms of:
- etiology and pathogenesis
- morphology
- laboratory findings
- clinical features and course
- complications
- Describe the principal clinical and morphologic findings in chronic liver disease.
- Compare and contrast the clinical and pathologic features of viral hepatitis
- Compare and contrast the clinical and pathologic features of:
- Discuss pathogenesis, morphology, clinical course of alcohol-induced liver diseases:
- Classify types of cirrhosis, in terms of:
- etiology
- pathogenesis
- morphologic pattern (gross and microscopic)
- relationship to neoplasia
- Compare and contrast the clinical and pathologic features of
- Discuss portal hypertension in terms of:
- etiologic factors
- pathogenesis
- clinical features and course
- Compare predictable and unpredictable drug induced liver disease.
- Describe the pathophysiologic mechanism whereby the following hepatotoxic drugs/chemicals cause liver injury:
- Compare and contrast the clinical and pathologic features of:
- Describe typical infectious liver diseases caused by bacteria, protozoa and helminths; in terms of clinical and morphologic findings.
- List causes of fatty change (steatosis) of the liver, in terms of:
- size of fat vacoules
- zonal distribution of fat
- Describe the etiopathogenesis and consequences of:
- Compare and contrast the clinical and pathological features of the following tumors:
- Describe cholelithiasis in terms of
- risk factors
- mechanisms of stone formation
- composition of stones
- morphology of stones and gallbladder
- clinical features
- complications, including those of therapy
- Compare and contrast acute and chronic cholecystitis, in terms of:
- epidemiology and associated diseases
- morphology
- clinical findings
- complications, including complications of therapy
- Compare and contrast empyema and hydrops of the gallbladder, in terms of:
- etiology
- pathogenesis
- morphology
- clinical findings
- Discuss carcinoma of the gallbladder and extrahepatic bile ducts, in terms of:
- epidemiology
- relationship to cholelithiasis
- morphology
- clinical findings and course
- Describe the indications, benefits, and hazards of liver transplantation.
- Describe the morphology of liver transplant rejection.
|