Case assignments by lab group and class day:
| |
TUESDAY |
THURSDAY |
Labs 1, 2, & 3 |
|
|
Labs 4 & 5 |
|
|
CASE NUMBER 139
Clinical History: During a routine physical examination, a 68-year-old man was found to have guaiac-positive stool. Colonoscopy revealed an ulcerated mass in the sigmoid colon. Laboratory analysis showed increased levels of serum alkaline phosphatase, lactate dehydrogenase and gamma glutamyltranspeptidase (GGT). (click here for information about these lab tests)
139-1. Which of the following is the MOST LIKELY explanation for these laboratory findings?
- Divergent differentiation has occurred
- The patient has hepatocellular carcinoma
- The patient has an acute hepatitis C infection
- The tumor has metastasized to bone
- The tumor has metastasized to the liver
ANSWER
Clinical history, part 2 (click here to open) (password is alkphos)
CASE NUMBER 521
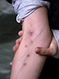
Clinical History: A 35-year-old man presents to the emergency department with a 2-week history of fever and jaundice. Physical exam reveals a thin man with skin lesions on his left arm.
Image Gallery:
The clinical image shows needle tracks, consistent with IV drug abuse.
|
|
|
521-1. What is the differential diagnosis?
ANSWER
521-2. Which tests would you order?
ANSWER
Clinical history, part 2 (click here to open) (password is biopsy)
Clinical history, part 3 (click here to open) (password is follow-up)
CASE NUMBER 81
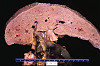
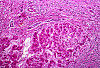
Clinical History:A 62-year-old alcoholic man presented to his primary care physician with a 3-month history of increased abdominal girth. Physical exam revealed telangiectasias and fluid wave of the abdomen. Laboratory findings showed elevated aminotransferase and decreased serum albumin; no other significant findings were noted. He was admitted to the hospital for further evaluation, but began retching violently with extensive hematemesis. Volume resuscitation failed and the patient died. Gross and microscopic images from the autopsy are provided.
Virtual Slide and Image Slide Gallery:
Slide 0081_Q: [ImageScope] [WebScope]
Norm No. 3
[ImageScope] [WebScope]
The liver is the organ that metabolizes nutrients received from the digestive tract. These nutrients and processed by tissue hepatocytes which are large polygonal cells. The hepatocyes are separated by portal triads. The triads consist of an artery, a vein and a bile duct. The bile duct is lined by cuboidal epithelium. The artery has a muscular wall and a flat endothelial lining. The sinuses are well defined and contain a small amount of blood.
|
(Summary of Gross Findings)
The liver weighed 1800 grams. The entire organ was uniformly composed of nodules about 0.5 cm in diameter, each surrounded by fibrous tissue. The organ was jaundiced and firm.
|
(Summary of Microscopic Findings)
The usual architecture present in the liver has been completely disrupted by the bands of connective tissue. In these bands one sees chronic inflammatory cells, mainly lymphocytes and other mononuclear cells. There is some proliferation of the bile ductules.
|
81-1. What is the differential diagnosis?
ANSWER
81-2. Which of the following is the most common cause of this disease?
- Chronic alcohol abuse
- Hepatitis B
- Hemachromatosis
- Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
- Wilson disease
ANSWER
81-3. Mallory bodies are intracytoplasmic accumulations of which of the following?
- Cytokeratin
- Desmin
- GFAP
- Glycogen
- Lipid
ANSWER
81-4. A patient with identical gross and microscopic findings is identified. However, his liver shows intracytoplasmic globules that are periodic acid-Schiff positive as shown below:
Which of the following additional findings would you expect?
- Anti-nuclear antibodies (ANAs)
- Decreased levels of serum ceruloplasmin
- Hepatic vein thrombosis
- PiZZ genotype
- Polycystic kidney disease
ANSWER
CASE NUMBER 89
Clinical History: A 73-year-old woman presented to the emergency department with a two-day history of right upper quadrant pain. Laboratory tests revealed an elevated WBC. Ultrasound evaluation showed gallstones present in the gallbladder and thickening of the gallbladder wall. A cholecystectomy was performed. Gross and microscopic images are provided.
Virtual Slide and Image Gallery:
Slide 0089_Q:
[ImageScope] [WebScope]
(Review Normal Histology) Webslide 0084_J: Gall bladder, monkey, H&E
[ImageScope] [WebScope]
The gall bladder is a distensible sac with extensive folds of mucosa that extend into the lumen. The mucosa consists of a tall, simple columnar epithelium and its underlying connective tissue (constituting a lamina propria). Note that there is NO SUBMUCOSA. The muscularis consists of scattered bundles of smooth muscle. Deep to the muscularis is an adventitia consisting of rather dense connective tissue that binds the gall bladder to the liver. Where the surface of the gall bladder faces the abdominal cavity there is a serosa.
|
(Summary of Gross Findings)
The gallbladder contained composite gallstones with a yellow to black appearance. Gallstones consist of a mixture of cholesterol, bilirubin, and calcium. Pure stones are uncommon, though jet black bilirubin stones suggest chronic hemolysis. The stones shown here are squared off (faceted) because they sat together. If gallstones obstruct the biliary duct, acute cholecystitis may develop.
|
(Summary of Microscopic Findings)
The gallbladder mucosa is acutely inflamed with many neutrophils in the epithelium and lamina propria. The epithelium is reactive with enlarged nuclei and abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm and ulcerated in some areas. There is hemorrhage and fibroblastic proliferation throughout the wall. Chronic cholecystitis is evidenced by plasma cells in the mucosa and Rokitansky-Aschoff sinuses which are diverticular invaginations of mucosa in the gallbladder wall. No tumor is seen.
|
89-1. What is the differential diagnosis?
ANSWER
89-2. Which of the following is the MOST COMMON cause of extrahepatic biliary obstruction?
- Bile duct carcinoma
- Carcinoma of the ampulla of Vater
- Carcinoma of the head of the pancreas
- Gallstones
- Phrygian cap
ANSWER
89-3. Which of the following is a risk factor for cholesterol-type gallstones?
- Age less than 25 years
- Asian ethnicity
- Male sex
- Obesity
- Sickle cell anemia
ANSWER
89-4. Which of the following is associated with chronic cholecystitis?
- Atrophy of the gallbladder wall
- Decreased risk of pancreatitis
- History of major trauma and burns
- Increased risk of carcinoma of the gallbladder
- Infection with Salmonella typhi
ANSWER
CASE NUMBER 93
Clinical History: A 50-year-old alcoholic man presented to the emergency department with severe epigastric pain that radiated to his back. He stated that he had had multiple similar episodes over the previous five years and had been hospitalized several times for pain management. At this admission, laboratory analysis showed elevated levels of serum amylase and lipase. The patient developed refractory shock, peritonitis and died. Gross and microscopic images from the autopsy are provided.
Virtual Slide and Image Gallery:
Slide 0093_Q:
[ImageScope] [WebScope]
(Review Normal Histology)
Norm No. 7 Pancreas
[ImageScope] [WebScope]
The pancreas is comprised of glandular tissue with endocrine and exocrine function. The exocrine pancreas contains lobular arrays of acini. The acinar secretions of the exocrine pancreas are collected by the pancreatic ducts. The ducts are surrounded by a small amount of connective tissue without inflammation or fibrosis (scarring).The endocrine pancreas resides in the islets which are regularly arranged and present within the pancreatic lobules.
|
(Summary of Gross Findings)
Fibrosis obscured some areas of pancreas architecture. Saponification of peripancreatic fat was seen in small foci.
|
(Summary of Microscopic Findings)
Several areas of fat necrosis with adjacent neutrophil infiltrate are seen, evidence of acute pancreatitis. In addition, some lobules of the pancreas show fibrosis and loss acini, evidence of chronic pancreatitis. In these areas, islets of Langerhans appear larger and more abundant. This is partly because they are resistant to injury and persist when acini are destroyed and partly because they undergo reactive hyperplasia.
|
93-1. What is the differential diagnosis?
ANSWER
93-2. Which of the following is the most common cause of this disease?
- Cystic fibrosis
- Alcoholism
- Annular pancreas
- Pancreas divisum
- SPINK1 mutation
ANSWER
93-4. Which of the following is the most likely sequela of this disease??
- Adenocarcinoma of the pancreas
- Aortic dissection
- Lymphoplasmacytic sclerosing pancreatitis
- Metastatic calcification
- Pancreatic pseudocyst
ANSWER
93-2. Which of the following laboratory values is usually the first to increase in this disease?
- Serum amylase
- Serum calcium
- Serum lipase
- Urinary ketones
- White blood cell count
ANSWER
CASE NUMBER 189
Clinical History: A 60-year-old man presented to his primary care physician with a 6-month history of intermittent abdominal pain. During the past three weeks, he had noticed chalky and greasy stools and that he felt itchy. Clinical history revealed an unintentional 20-pound weight loss over the previous two months that he attributed to decreased appetite. Physical exam showed icterus. MRI revealed a mass in the head of the pancreas and the patient underwent surgical resection of this mass. Gross and microscopic images are provided.
Virtual Slide and Image Gallery:
Slide 0189_Q: [ImageScope] [WebScope]
(Review Normal Histology)
Norm No. 7 Pancreas
[ImageScope] [WebScope]
The pancreas is comprised of glandular tissue with endocrine and exocrine function. The exocrine pancreas contains lobular arrays of acini. The acinar secretions of the exocrine pancreas are collected by the pancreatic ducts. The ducts are surrounded by a small amount of connective tissue without inflammation or fibrosis (scarring).The endocrine pancreas resides in the islets which are regularly arranged and present within the pancreatic lobules.
|
(Summary of Gross Findings)
The head of the pancreas was enlarged with yellow-gray firm tissue, in which no normal lobular structures were seen. About 4 cm proximal to the ampulla there was a stenosis of the common bile duct. Proximal to this stenosis the bile ducts were markedly dilated with bile. The peripancreatic lymph nodes and the celiac axis were gray and firm with metastastic tumor.
|
(Summary of Microscopic Findings)
The tumor is composed of duct-like structures, which are irregularly arranged and infiltrate into the dense connective stroma and perivascular or perineural lymphatics. Occasionally both ducts and individual tumor cells contain mucin. There is a small amount of pancreatic tissue which shows marked atrophy and fibrosis. The small ducts are distended and may show focal squamous metaplasia of the epithelium in some sections.
|
189-1. What is the differential diagnosis?
ANSWER
189-2. Which of the following is most commonly mutated in this disease?
- BRCA2
- GNAS
- KRAS
- SMAD4
- VHL
ANSWER
189-3. Which of the following is usually a precursor lesion for this disease?
- Acute pancreatitis
- Chronic pancreatitis
- Pancreatic intraepithelial neoplasia
- Pancreatic pseudocysts
- Serous cystadenoma
ANSWER
PANCREAS Review Items
Key Vocabulary Terms (click here to search any additional terms on Stedman's Online Medical Dictionary)
LEARNING OBJECTIVES
Absolutely critical information you must know to practice medicine is in bold font.
Important information that will be needed for routine patient care is in regular font.
Information about less common diseases that you may encounter in clinical practice and that will probably appear on examinations is in italics
- Compare and contrast the clinical and pathologic features of:
- Discuss the clinical and pathologic features of cystic fibrosis.
- Compare and contrast acute and chronic pancreatitis, in terms of:
- etiologic/predisposing factors
- pathogenesis
- morphologic features
- laboratory manifestations
- clinical findings and course
- complications
- Compare and contrast the clinical and pathologic features of adenocarcinoma of the:
- pancreatic head
- pancreatic body/tail
- ampulla of Vater
- 5. Discuss islet cell tumors of the pancreas, in terms of:
- incidence
- morphology
- benignity vs. malignancy
- immunohistochemical characteristics
- endocrine function
- clinical features and course
- Discuss indications and complications of pancreatic islet cell transplantion.
LIVER and BILIARY TRACT Review Items
Key Vocabulary Terms (click here to search any additional terms on Stedman's Online Medical Dictionary)
LEARNING OBJECTIVES
Absolutely critical information you must know to practice medicine is in bold font.
Important information that will be needed for routine patient care is in regular font.
Information about less common diseases that you may encounter in clinical practice and that will probably appear on examinations is in italics
- Describe the formation of bile and explain abnormalities that could cause jaundice.
- Discuss the clinical indications for the following laboratory tests:
- Compare and contrast the clinical and pathologic features of
- Compare and contrast biliary atresia and neonatal hepatitis, in terms of:
- etiology and pathogenesis
- morphology
- laboratory findings
- clinical features and course
- complications
- Describe the principal clinical and morphologic findings in chronic liver disease.
- Compare and contrast the clinical and pathologic features of viral hepatitis
- Compare and contrast the clinical and pathologic features of:
- Discuss pathogenesis, morphology, clinical course of alcohol-induced liver diseases:
- Classify types of cirrhosis, in terms of:
- etiology
- pathogenesis
- morphologic pattern (gross and microscopic)
- relationship to neoplasia
- Compare and contrast the clinical and pathologic features of
- Discuss portal hypertension in terms of:
- etiologic factors
- pathogenesis
- clinical features and course
- Compare predictable and unpredictable drug induced liver disease.
- Describe the pathophysiologic mechanism whereby the following hepatotoxic drugs/chemicals cause liver injury:
- Compare and contrast the clinical and pathologic features of:
- Describe typical infectious liver diseases caused by bacteria, protozoa and helminths; in terms of clinical and morphologic findings.
- List causes of fatty change (steatosis) of the liver, in terms of:
- size of fat vacoules
- zonal distribution of fat
- Describe the etiopathogenesis and consequences of:
- Compare and contrast the clinical and pathological features of the following tumors:
- Describe cholelithiasis in terms of
- risk factors
- mechanisms of stone formation
- composition of stones
- morphology of stones and gallbladder
- clinical features
- complications, including those of therapy
- Compare and contrast acute and chronic cholecystitis, in terms of:
- epidemiology and associated diseases
- morphology
- clinical findings
- complications, including complications of therapy
- Compare and contrast empyema and hydrops of the gallbladder, in terms of:
- etiology
- pathogenesis
- morphology
- clinical findings
- Discuss carcinoma of the gallbladder and extrahepatic bile ducts, in terms of:
- epidemiology
- relationship to cholelithiasis
- morphology
- clinical findings and course
- Describe the indications, benefits, and hazards of liver transplantation.
- Describe the morphology of liver transplant rejection.
|